Today I came across an interesting article in the Wall Street Journal. I've spent much of the day trying to track down background information and, thus far, appear to have only scratched the surface.
The initial article was titled "Hungry? Your stomach really does have a mind of its own." It described an research effort by scientists working for the Nestle SA company, a huge firm headquartered in Switzerland, but operating in 86 countries and employing well over a quarter million people.
When I think of Nestle, I think of chocolate, but they started with condensed milk and baby formulas. They've done some praiseworthy things and some that have been severely criticized. Among the former are efforts to halt child labor in cocoa production; the latter includes promotion of the use of infant formula to mothers in developing countries.
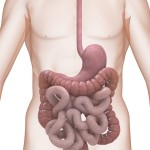
The article I was reading talked about satiety factors to stop us from overeating. Nestle has a group of its scientists working on foods that potentially can trick what is termed the gut brain. That's known to physicians as the enteric nervous system, a huge collection of nerve cells involved in actions and reactions in the GI tract: the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
So here's how it works, or at least some of how it functions, in hunger and satiety. Eating stretches the stomach, causing "I'm full" messages to be sent to the real brain, the one in your head. Chemicals called peptides are released when food is present in the intestine; that also signals the brain. Then there's another mechanism I'd never heard of, one called the "Ileal Brake."
The ileum is part of the small intestine and apparently another "I'm full" message can be sent upstairs when there is an excess of fat reaching that part of the gut, in this case excess means more than can be handled (processed) at the moment.
So the Nestle scientists developed a mechanical model of the human GI system, one that cost a million dollars, is the size of a really big refrigerator and is computer-controlled. Using this machine, their lead scientist, Heribert Watzke, and his crew are simulating the progress of a meal through our GI tracts.
I found a video of Dr. Watzke speaking to what appeared to me to be a mostly college-age audience at Oxford, England. He's a very entertaining speaker, obviously partakes a bit too much of his own company's products (or other food) and admits this. He thinks we shouldn't be called omnivores, but rather "Coctivores," creatures that eat cooked food.
His premise is that cooking allowed mankind to develop larger brains and freed them to be able to move around the planet. He wasn't speaking of the food products his company produces, but rather presented a formula: food + cooking = energy.
I need (pun intended) to digest this concept a little more; I'll return to it at a later time.
Meanwhile I suggest you Google Dr. Watzke and observe his show.

Located your website through Digg. You already know I am subscribing to your rss feed.
Oh gosh, I disagree, but, nonetheless, it's an interesting experience, RRS subscribed!